Diamond Gallery
On this page you can get an impression of the broad variety of possible
applications of Diamond. Every picture is also available as '.dsf' file, which
you can download and explore using the Diamond Demo version.
In addition you can inspect the scenes using VRML viewers.
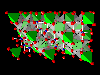
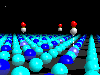
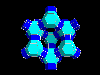
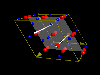
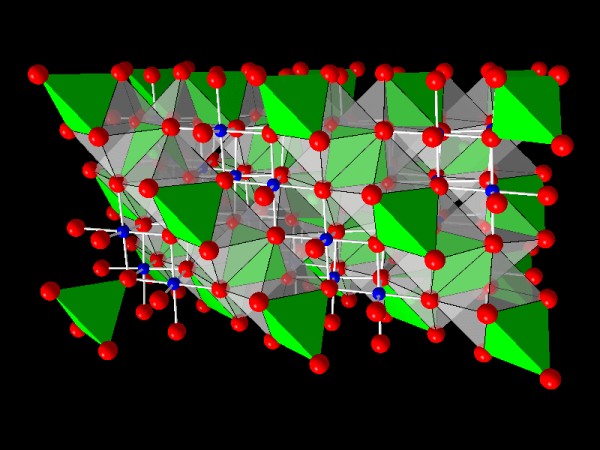
In the spinel-type structure of MgAl2O4, Mg-ions occupy
tetrahedral-shaped cavities within the oxygen framework (green tetrahedrons)
whereas 50% of the octahedral-shaped cavities are occupied by Al-ions (blue).
Using dummy atoms (invisible because radius set to zero) as centers of
translucent coordination polyhedra it is easy to visualize even the unoccupied
cavities.
Click here for download of the Diamond '.dsf' file:
spinel.dsf (41 KB)
Click here for VRML file: spinel.wrl
(411 KB)
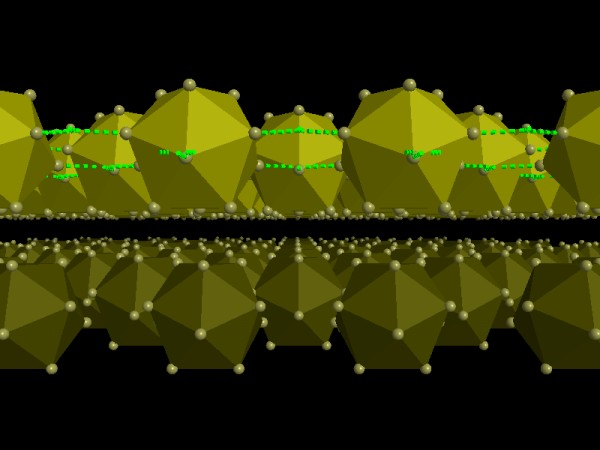
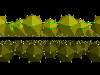
View between two layers of boron icosahedras. In the upper layer the green
broken lines indicate the delocalized 2-electron-3-center bonds between the
icoshedras. The centers of the delocalized bonds were 'constructed' using dummy
atoms (structure data taken from the ICSD).
Click here for download of the Diamond '.dsf' file:
boron.dsf (251 KB)
Click here for VRML file: boron.wrl
(4953 KB)
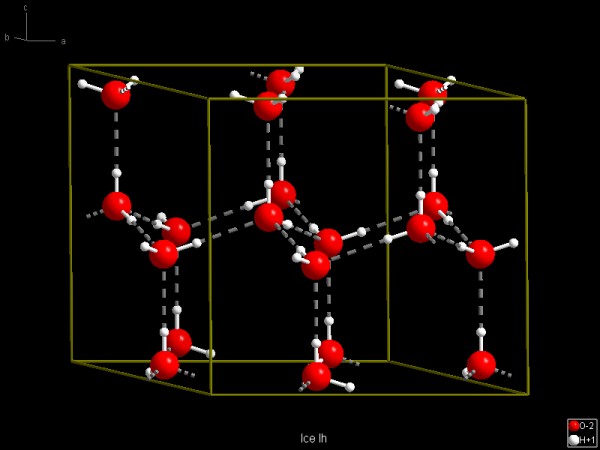
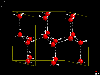
Having control over connectivity criteria and bond designs allows easily
localization and display of hydrogen bonds - as shown here in a hexagonal ice
modification (structure data taken from the ICSD).
Click here for download of the Diamond '.dsf' file:
ice.dsf (9 KB)
Click here for VRML file: ice.wrl
(66 KB)
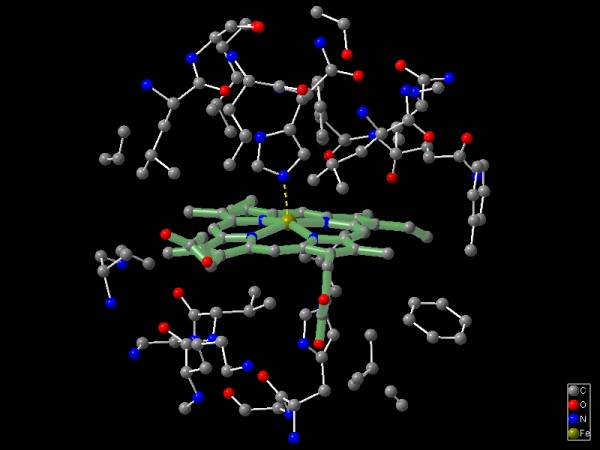
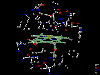
Exploring a 10 Angstrom sphere around the iron atom within the hemoglobine
molecule shows the geometric details of the area responsible for the essential
oxygen transport (data taken from the PDB).
Click here for download of the Diamond '.dsf' file:
hemoglobine.dsf (327 KB)
Click here for VRML file: hemoglobine.wrl
(92 KB)
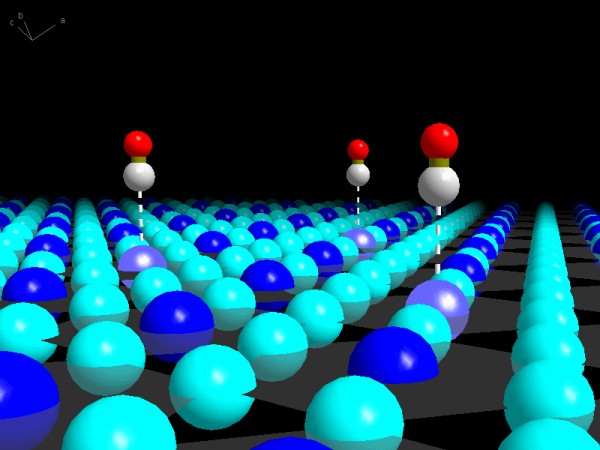
Using the free cartesian XYZ format allows easy data exchange with other
software (e.g. modelling programs). This example shows CO molecules 'on-top'
coordinated to Pt atoms within a (111) surface of Cu3Pt. The surface was
prepared with Diamond (data taken from Pauling File)
Click here for download of the Diamond '.dsf' file:
surface.dsf (207 KB)
Click here for VRML file: surface.wrl
(1503 KB)
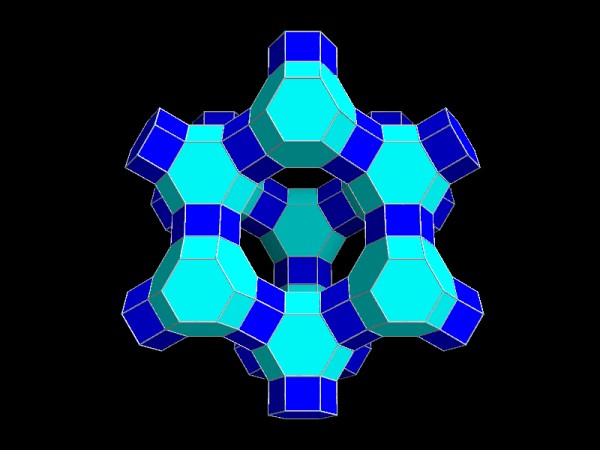
Having control over connectivity criteria and using filters it is easy to
construct complex polyhedra frameworks like this Faujasite example (data taken
from ICSD).
Click here for download of the Diamond '.dsf' file:
faujasite.dsf (45 KB)
Click here for VRML file: faujasite.wrl
(779 KB)
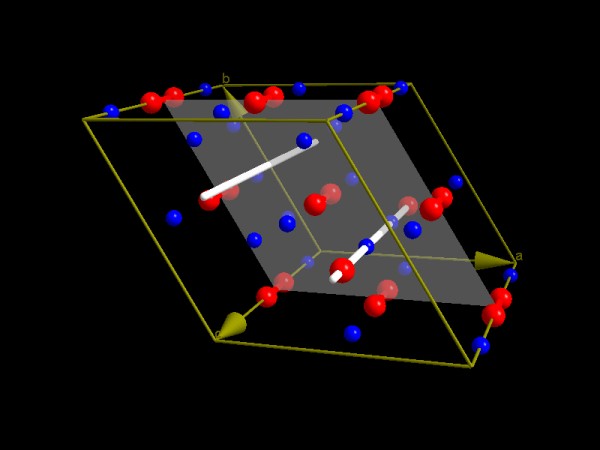
Though DIAMOND has no special feature for the automatic presentation of symmetry
elements, it is easily possible to visualize them as shown in this example of
hexagonal Lithiumperoxide with six-fold rotation axes and the corresponding
mirror plane (spacegroup P-6; data taken from ICSD).
Click here for download of the Diamond '.dsf' file:
symmetry.dsf (7 KB)
Click here for VRML file: symmetry.wrl
(21 KB)
|

